Everything you need to know about tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease which mainly is caused due to the bacteria mycobacterium which affects the lung. Since the bacteria spreads through the air, it can spread through coughs, sneezes, or even as the person speaks. The bacteria cannot survive on the surface, tuberculosis does not spread through shaking hands, sharing a bathroom, shaking glasses or eating utensils.
Symptoms
Although the body may not harbor the bacteria causing tuberculosis, doctors classify symptoms based on the response of the immune system:
- Latent TB
The bacteria remains in the body in an active state and cause no symptoms. Latent TB is not contagious but can turn active if not met with timely treatment. - Active TB
This type of TB is contagious and can occur in the first few weeks after getting infected with the bacteria. The signs and symptoms of active TB include: coughing that lasts for at least a month, blood in cough, chest pain, fatigue, fever, chills, loss of appetite, and night sweats.
Tuberculosis can also affect other parts of the body including, spinal cord, kidneys, and brain. For instance, tuberculosis in the kidneys might cause blood in urine and tuberculosis of the spine might cause back pain.
Risk factors
The following factors can increase the risk of getting infected from the disease:
- Weakened immune system
A body cannot mount an effective defense if the resistance is low. Diseases such as HIV/AIDS, severe kidney infection, cancer treatment such as chemotherapy, diabetes, malnutrition can result in a weakened immune system. Apart from this, medicines to treat rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and psoriasis or prevent rejection of transplanted organs can also weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of tuberculosis. - Substance abuse
Alcohol abuse and IV (intravenous) drug use and excessive use of tobacco increases the risk of suffering from tuberculosis and can also prove to be fatal.
Complications
Chronic symptoms of tuberculosis can cause spinal pain. It also causes arthritis which usually affects the knees and hips. Tuberculosis also causes swelling of membranes covering the brain resulting in a lasting and intermittent headache. The infection can also infect the tissues surrounding the heart, interfering with its ability to pump efficiently.
Diagnosis
Following diagnostic procedures can help confirm the infection due to tuberculosis:
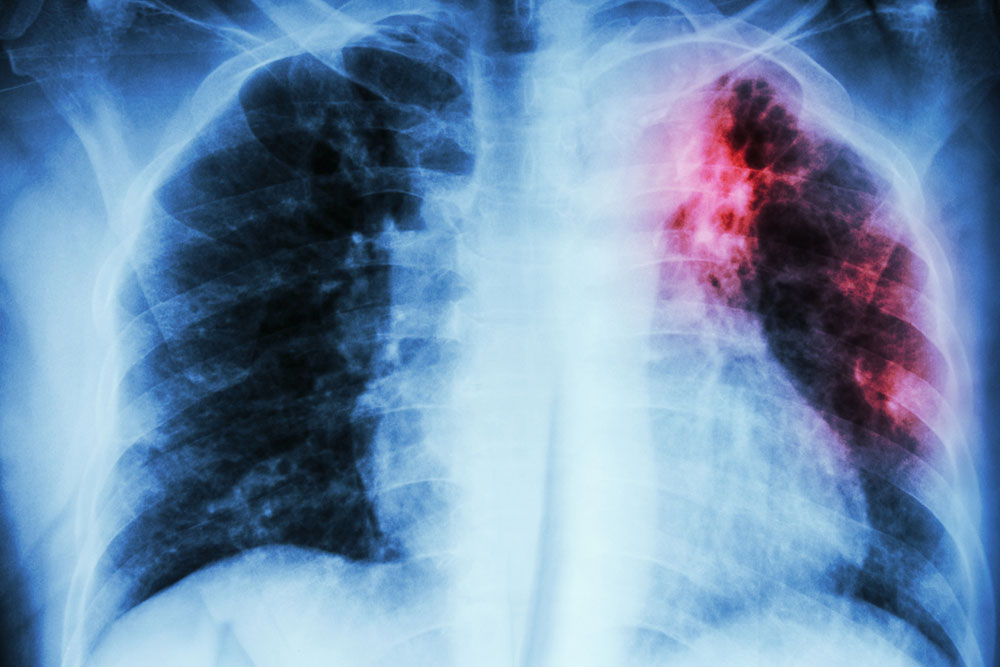
- Imaging test
If the person has had a positive skin test, the doctors will likely order a chest x-ray and CT scan. The white spots in the lungs show active spots of tuberculosis. - Blood tests
These are used to confirm latent or active tuberculosis. - Sputum tests
These are specifically used for drug resistant strains of Tuberculosis, thereby helping the doctors to prescribe medicines.
Treatments
A patient with tuberculosis should take antibiotics for at least six months. The dosage of antibiotics depend upon the patients age, overall health. Recent developments in the medical field requires the patient to take the medications for a shorter period. Combination of medications help in keeping latent TB from becoming active TB. It is important to discuss about the side effects with the doctor so that they can suggest remedies to manage the same. Some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, jaundice, dark urine, and persistent fever.




