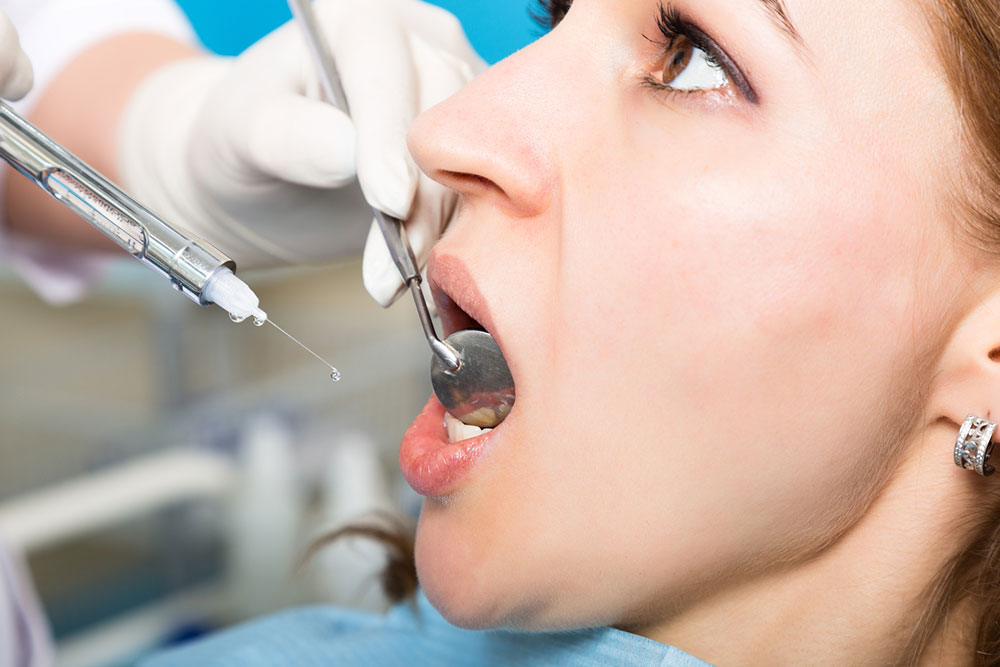
An overview of tooth cavities
A cavity, commonly also known as tooth decay, is a hole that forms in your tooth. Cavities start small and get bigger gradually if left untreated. It can be difficult to identify cavities in their initial stages as they do not cause any pain in the beginning. Regular dental appointments can detect any form of tooth decay at a comparatively early stage. Hence, it is important to visit your dentist every once a while.
According to a number of studies, cavities or tooth decay fall under the category of most common health problems in the world. Cavities can affect people from any age group right from babies to adults up to old age. If you follow a good oral hygiene routine, discovering that you have developed a cavity might more than often come around as a surprise. But there are numerous ways in which a cavity can be treated, and new ones can be prevented from getting formed. Cavities usually cause symptoms such as
- Pain in the tooth
- Sensitivity of the tooth
- A visible hole in your teeth
- Excessive black or white staining on your teeth
A tooth cavity is usually caused due to the plaque which is a sticky substance that binds to the teeth. Plaque is a combination of acid, food particles, saliva, and bacteria. Each one of us has bacteria in our mouth. After drinking or eating sugary foods, these bacteria turn the sugar in the mouth to acids which leads to the formation of plaque. This is why it is paramount that one brushes their teeth and rinses their mouth regularly. Everyone is at a risk for tooth cavities, but certain people have a higher risk of developing them. A few common causes of developing cavities are
- A poor oral hygiene routine such as failing to floss or brush on a regular basis
- The consumption of too many acidic or sugary foods and drinks
- Not getting fluoride in sufficient amounts
- Dry mouth
- Eating disorders like anorexia and bulimia
- Acid reflux disease that can result in wearing down the tooth’s enamel due to the acid in your stomach
A tooth cavity can cause a number of complications if left untreated. Some of these complications include
- Pus development around the infected tooth
- An increased risk of chipping or breaking a tooth
- Ongoing pain in the tooth
- A tooth abscess which can trigger life-threatening complications such as infections that enter the sepsis or bloodstream.
- Difficulty in chewing food
You may end up causing irreversible damage to your tooth if you put off seeing a dentist under such circumstances. At this point, the only way to fix the cavity is for your dentist to remove the affected tooth and replace it with a bridge or implant. Remember, maintaining good oral hygiene and going for regular check-ups will go a long way in preventing cavities from getting severe in the first place.




